Some of the links in this post may be affiliate links, which means I may receive a commission if you click on them and make a purchase. However, this comes at no additional cost to you, and I only recommend products and services that I truly believe in. Please note that I am not responsible for the quality, accuracy, timeliness, reliability, or any other aspect of the products and services sold on external websites linked to this post.
Heavy metals, such as lead, mercury, arsenic, and cadmium, are toxic substances that can build up in our bodies over time, resulting in a wide range of health problems. These harmful metals can be found in various sources, including contaminated water, tap water, air pollution, foods, dental fillings, and even beauty and household products. It is crucial to understand how heavy metals can enter our bodies in order to take steps to reduce their detrimental effects.
Our story
In my oldest son’s early years, it was obvious that he was a little different than the “average” toddler. He didn’t play with other kids, and he didn’t talk (and I don’t mean he never talked; he knew how to say words that we taught him. But he wouldn’t talk outside of that unless he was asking for basic things like juice, milk, snacks, foods, etc.), and at any social element, he would melt into my lap like he wasn’t there. I often experienced judgment from others about these behaviors. As if I hadn’t already noticed that my son was there but not there. As if I couldn’t tell my son wasn’t playing like the rest of the others. As if I didn’t already notice how my son won’t make eye contact or acknowledge your existence.
He had all the routine tests like lead testing, and his levels weren’t in a concerning range. His doctor wasn’t concerned with his development until we brought up the possibility of an autism diagnosis. Then the dots seemed to start to connect in his brain. He didn’t want to push for a diagnosis right away, and he recommended an outside foundation to dig further. But all in all, his doctor seemed to want to put a pin in the process for the time being.
It wasn’t until a few years later that I was introduced to an herbal detox that specifically targets heavy metals. I purchased a small bottle and began our journey of detox! After about 4 months of detoxing, we began to notice a change in him. And the biggest validation was when extended family during a Christmas get-together, commented on his change! My son was holding conversations and making eye contact, and even playing around with the family. To see your son go from nearly non-verbal to holding a conversation with not just his parents but with others is nothing short of tearfully joyful!
Where are heavy metals?
Children and infants can be exposed to heavy metals through various sources, including:
- Lead-based paints and dust: Lead-based paints used in older homes, particularly those built before 1978 when lead-based paints were banned in the United States, can deteriorate over time and release lead-containing dust particles that can be ingested or inhaled by children. Children can also be exposed to lead-containing dust brought home on the clothes or shoes of adults who work in certain industries or engage in hobbies involving lead-based materials.
- Contaminated soil and water: Children who play in soil or ingest water from contaminated sources, such as those near industrial areas, mining sites, tap water, or contaminated wells, may be at risk of heavy metal exposure.
- Food and beverages: Certain foods and beverages, particularly those grown or processed in contaminated environments, may contain elevated levels of heavy metals. This can include fish from polluted waters, rice from areas with high levels of arsenic in the soil, and foods processed with contaminated water or equipment.
- Consumer products: Some consumer products, such as toys, jewelry, cosmetics, and imported goods, may contain heavy metals as contaminants or intentional additives.
What are the signs of heavy metal toxicity in little ones?
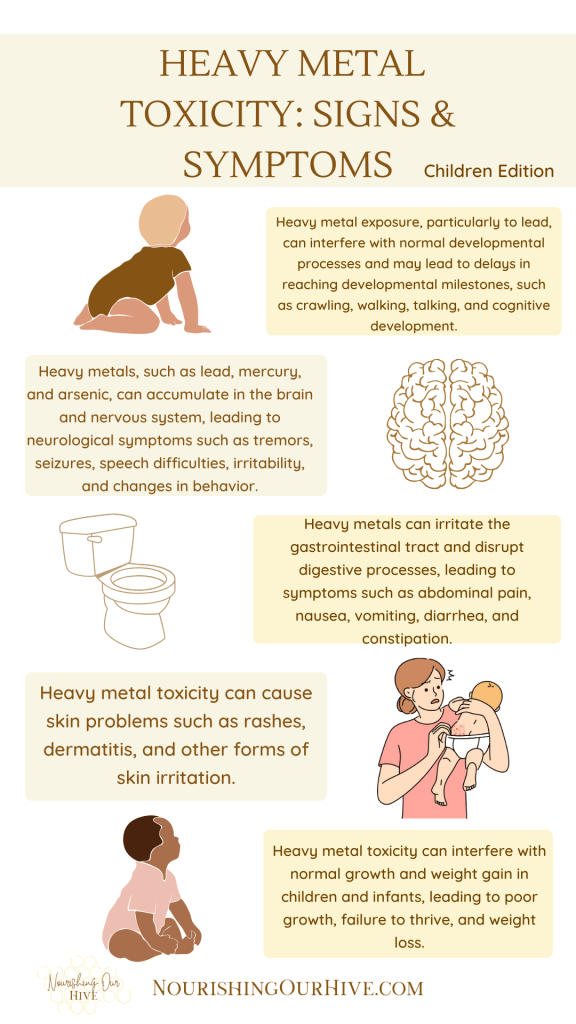
Heavy metal toxicity in children and infants can manifest in various ways and may present a wide range of signs and symptoms, which can vary depending on the type of heavy metal, the duration and level of exposure, and individual susceptibility. Some common signs and symptoms of heavy metal toxicity in children and infants may include:
- Developmental delays: Heavy metal exposure, particularly to lead, can interfere with normal developmental processes and may lead to delays in reaching developmental milestones, such as crawling, walking, talking, and cognitive development.
- Neurological symptoms: Heavy metals, such as lead, mercury, and arsenic, can accumulate in the brain and nervous system, leading to neurological symptoms such as tremors, seizures, speech difficulties, irritability, and changes in behavior.
- Cognitive impairments: Heavy metal toxicity can affect cognitive function, leading to problems with memory, attention, concentration, and learning difficulties.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Heavy metals can irritate the gastrointestinal tract and disrupt digestive processes, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation.
- Behavioral and mood changes: Heavy metal exposure can affect mood and behavior in children and infants, leading to symptoms such as irritability, mood swings, aggression, and changes in sleep patterns.
- Growth and weight issues: Heavy metal toxicity can interfere with normal growth and weight gain in children and infants, leading to poor growth, failure to thrive, and weight loss.
- Respiratory issues: Inhalation of heavy metal particles or fumes can irritate the respiratory system and lead to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and respiratory distress.
It’s important to note that heavy metal toxicity can be subtle and may not always present with specific symptoms, and some children may be more susceptible to the effects of heavy metals due to various factors such as genetics and overall health. If you suspect heavy metal toxicity in your child or infant, it’s essential to consult with a qualified holistic healthcare professional for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment.
What can we do?
I covered this in my last blog post, but I can reiterate it here for you all!
One powerful natural detoxifier is chlorella, a type of freshwater algae known for its ability to bind to heavy metals and facilitate their removal from the body. Chlorella has a unique cell wall structure that allows it to bind to heavy metals like mercury, lead, and cadmium in the digestive tract, preventing their absorption into the bloodstream. Chlorella also contains essential nutrients like chlorophyll, vitamins, and minerals, which can support overall health and well-being. Hello, little powerhouse!
Another herb that has been traditionally used for detoxifying heavy metals is Oregon grape root. Oregon grape root contains a compound called berberine, which has been shown to have strong antioxidant and detoxifying properties. Berberine has the ability to bind to heavy metals and promote their elimination from the body through urine and feces. Additionally, Oregon grape root can also support liver function, which plays a crucial role in the body’s detoxification processes. The perfect all-in-one detox herb! When detoxing, supporting your detox pathways (a big one being your liver!) is crucial.
One of the products I mentioned earlier contains both Chlorella and Oregon Grape Root alongside other herbs that help support our bodies and immune system while detoxing. You can check it out here! This product is safe for ages 1 and up.
In addition to chlorella and Oregon grape root, there are several other herbs and supplements that can support the body’s detox pathways and aid in heavy metal detoxification. These include cilantro, milk thistle, garlic, and N-acetyl cysteine (NAC). Cilantro, commonly used as an herb in cooking, has been shown to have chelating properties, helping to mobilize and eliminate heavy metals from the body. Milk thistle is known for its liver-protective properties, which can support the liver in processing and eliminating heavy metals. Garlic, a well-known culinary herb, has antioxidant properties that can help neutralize heavy metals and promote their elimination. NAC is a powerful antioxidant that can increase the production of glutathione, a critical antioxidant in the body that plays a role in heavy metal detoxification.

Resources
- “A Review on Chlorella- A Nutraceutical Algae” – International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences (https://innovareacademics.in/journals/index.php/ijpps/article/view/18929/12413): This scientific article provides an in-depth review of chlorella, including its nutritional value, potential health benefits, and its role in detoxification, supported by scientific research.
- “Berberine: An Alternative Approach for the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome” – Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5852681/): This scientific article discusses the potential health benefits of berberine, including its antioxidant and detoxifying properties, supported by scientific studies.
- “The Role of Glutathione in Detoxification” – Environmental Health Perspectives (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1242206/): This scientific article provides an overview of the role of glutathione, a critical antioxidant in the body, in detoxification processes, supported by scientific evidence.
- “Toxic Metal Exposure as a Cause of Parkinsonian Symptoms” – Environmental Health Perspectives (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1637782/): This scientific article discusses the potential health risks of heavy metal exposure, including their impact on neurological health, supported by scientific research.
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) – Heavy Metals: The ATSDR is a federal public health agency in the United States that provides comprehensive information on toxic substances, including heavy metals. Their website offers in-depth information on various heavy metals, their sources, health effects, exposure pathways, and recommendations for exposure prevention and management. (Website: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxfaqs/index.asp)
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – Heavy Metals: The EPA provides information on heavy metals, including their sources, environmental impact, and regulations related to heavy metal contamination. Their website offers resources on heavy metals such as lead, mercury, arsenic, and cadmium, and their potential health risks. (Website: https://www.epa.gov/chemical-research/heavy-metals)
- World Health Organization (WHO) – Heavy Metals: The WHO offers authoritative information on heavy metals, including their sources, health effects, exposure assessment, and risk management. Their website provides global guidelines and recommendations on heavy metal exposure limits and mitigation strategies. (Website: https://www.who.int/occupational_health/topics/metals/en/)

